—
# October Sees Highest Layoff Surge Since 2003: Key Insights and Implications
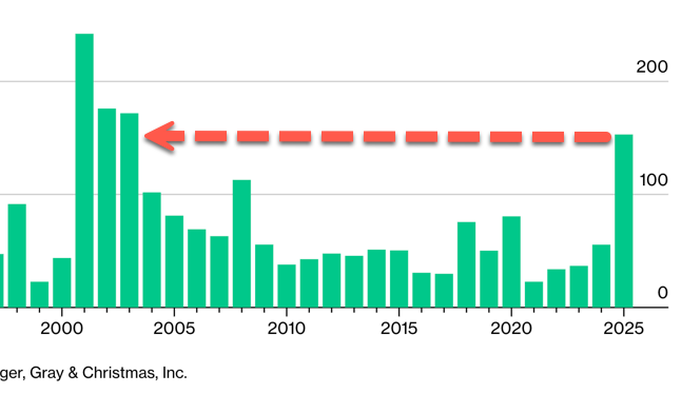
The U.S. labor market experienced a notable downturn in October, with companies announcing a staggering 153,000 job cuts. This figure represents an alarming 175% increase from the same month last year and marks the highest number of layoffs in October since 2003, according to data from outplacement firm Challenger, Gray & Christmas. This article delves into the causes behind these layoffs, the industries most affected, and what this means for the economy moving forward.
## Key Drivers Behind the Layoff Surge
### 1. **Pandemic Overhiring Correction**
Many of the layoffs can be attributed to a correction following the overhiring that occurred during the pandemic. Companies expanded their workforce to meet increased demand but are now reevaluating their staffing needs in response to changing market conditions. The technology and warehousing sectors, in particular, have seen significant cuts as businesses streamline operations.
### 2. **Cost-Cutting Measures**
Rising operational costs and slowing consumer demand have prompted companies to adopt aggressive cost-cutting strategies. In October, cost-cutting was cited as the primary reason for 50,437 layoffs. This trend highlights a broader shift in corporate strategies as businesses prioritize profitability amid economic uncertainty.
### 3. **Artificial Intelligence Adoption**
AI continues to reshape the workforce. In October alone, AI-related restructuring led to 31,039 job cuts, reflecting a growing trend among companies to automate processes and improve efficiency. As AI technology advances, businesses are rethinking their workforce composition, resulting in further layoffs.
## Industries Most Affected
### 1. **Technology Sector**
The technology industry faced the brunt of the layoffs, with 33,281 job cuts in October, a substantial increase from 5,639 in September. Year-to-date, the sector has seen 141,159 layoffs, representing a 17% increase compared to last year.
### 2. **Warehousing**
The warehousing sector recorded 47,878 layoffs in October, a stark rise from just 984 in September. This surge indicates a significant adjustment as companies address excess capacity and the impact of automation.
### 3. **Retail and Consumer Products**
While retail saw a slight decrease in job cuts month-over-month, it still reported 2,431 layoffs in October, contributing to a year-to-date total of 88,664. The consumer products sector also experienced cuts, totaling 3,409 layoffs in October.
## Implications for the Labor Market
### **A Shift to Low-Hiring, High-Firing**
The data suggests a worrying trend in the labor market: a shift towards a “low-hiring, high-firing” environment. With the year-to-date job cuts surpassing 1 million—the highest level since 2020—and hiring plans at their lowest since 2011, the outlook appears bleak. Companies are increasingly hesitant to expand their workforce, and those who have been laid off may find it challenging to secure new employment quickly.
### **Potential Economic Consequences**
The implications of this labor market shift extend to the broader economy. As consumer spending slows and corporate costs rise, businesses may struggle to maintain profitability, potentially leading to further economic downturns. Analysts suggest that this could influence monetary policy, with expectations for potential interest rate cuts to stimulate growth.
## Actionable Takeaways for Businesses
1. **Reevaluate Workforce Needs**: Companies should take a critical look at their staffing levels and consider whether they need to adjust their workforce in light of recent economic trends.
2. **Invest in Automation**: As AI adoption continues to reshape industries, businesses should explore automation solutions that can enhance productivity without compromising workforce stability.
3. **Monitor Economic Indicators**: Stay informed about consumer spending patterns and economic conditions. This knowledge will be vital for making informed decisions regarding hiring and operational strategies.
4. **Prepare for Economic Uncertainty**: With the labor market shifting, businesses should develop contingency plans to navigate potential economic challenges, including cash flow management and cost control measures.
In conclusion, the surge in layoffs during October serves as a critical indicator of the current state of the U.S. labor market. As companies adapt to new realities shaped by AI and economic pressures, stakeholders must remain vigilant and proactive in their strategies to mitigate risks and seize opportunities.