—
## America’s Declining Population: Economic Implications and Opportunities
### Understanding the Demographic Shift
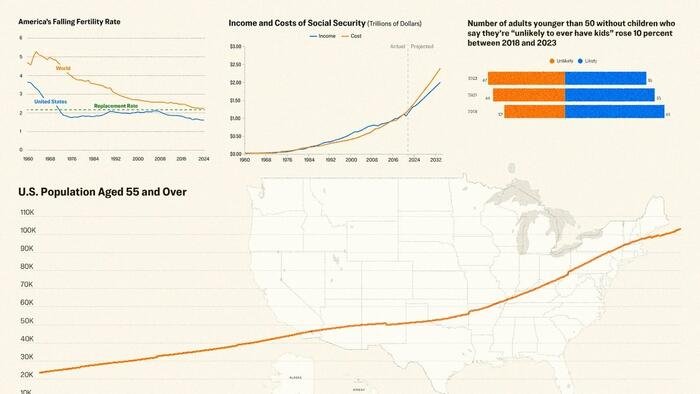
Recent data reveals a significant demographic transition in the United States: the population is aging, and birth rates are falling. Currently, adults aged 65 and older are projected to reach 82 million by 2050, making up 23% of the population—a 42% increase from 2022. Concurrently, the fertility rate has plummeted from 3.1 births per woman in 1950 to just 1.6 in 2023. This demographic squeeze poses critical challenges for the economy and infrastructure over the coming decades.
### Economic Consequences of an Aging Population
Economists are increasingly concerned that the decline in fertility rates will create an economic burden. As the number of retirees grows and the workforce shrinks, the younger generation will face the dual challenge of supporting a larger retired population while experiencing lower economic growth. For instance, the Social Security Administration has warned that the program may become insolvent by 2034, with costs exceeding revenues by $437 billion.
**Actionable Takeaway:** Businesses and policymakers should prepare for a shifting economic landscape by investing in automation and technology to offset labor shortages, while also advocating for policies that encourage family growth and support for working parents.
### Healthcare Industry Upheaval
The healthcare sector is already feeling the effects of this demographic shift. With a projected shortage of 3.2 million healthcare workers by 2026, the industry is underprepared for the increasing demands of an aging population. The rise of the “longevity business”—encompassing biotech, wellness, and regenerative medicine—highlights both an opportunity and a threat. While this sector is set to become a multibillion-dollar industry, it also underscores the strain on existing healthcare resources.
**Actionable Takeaway:** Healthcare providers should focus on innovative staffing solutions and invest in training programs for younger workers to bridge the skills gap. Additionally, businesses in the longevity space can explore partnerships with healthcare providers to develop integrated care solutions.
### Labor Market Transformation
The labor market is undergoing a dramatic transformation as fewer younger workers enter the workforce. Interestingly, adults over 55 are choosing to work longer, with 74% expressing a desire to continue working. This shift may redefine the traditional concept of retirement, as many older adults seek purpose and financial stability.
**Actionable Takeaway:** Companies should consider creating flexible work arrangements and retraining programs to attract older workers. Emphasizing the value of experienced employees can enhance workforce diversity and productivity.
### The Psychological Impact of Declining Birth Rates
The phenomenon of “procreative dissonance” is emerging as a psychological barrier to higher birth rates. Many individuals feel biologically capable of parenthood but are deterred by societal pressures and economic realities. The CDC reports a decline in birth rates among younger women, while older women are increasingly having children.
**Actionable Takeaway:** To address declining birth rates, businesses and policymakers should foster a family-friendly environment through parental leave policies, childcare support, and financial incentives for families. This approach can help create a more supportive culture for parenting.
### Conclusion: Preparing for the Future
America’s declining population presents both challenges and opportunities across various sectors. The economic implications of an aging population, coupled with the need for a more adaptable labor market and healthcare system, necessitate proactive strategies. By investing in workforce development, healthcare innovation, and family-friendly policies, stakeholders can mitigate the adverse effects of demographic changes and position themselves for success in a rapidly evolving landscape.